Building stronger strategic partnerships in R&D
7 min read 2 May 2024
In today's competitive pharmaceutical and life sciences landscape, the establishment of strategic partnerships is increasingly recognised as a means to enhance innovation and drive future growth within research and development (R&D).
Strategic partnerships represented three of the top 10 highest value R&D projects in 20231, and they will only become more critical as major pharma industry players face upcoming patent expiries and recognise the need to diversify and replenish their pipelines2.
What is a strategic partnership?A strategic partnership in R&D refers to a mutually beneficial collaboration or alliance between two or more organisations, such as pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions, or biotech firms, with the aim of jointly pursuing R&D activities to achieve shared research outcomes. These partnerships involve the pooling of resources, expertise, and capabilities to accelerate innovation, enhance scientific knowledge, and address complex challenges across research and clinical development. |
Forming strategic partnerships with external entities can provide advantages that cannot be achieved solely through internal efforts or through acquiring other companies:
- Sharing financial burden: Strategic partnerships allow organisations to distribute the financial burden associated with research and development (R&D), clinical trials, and regulatory filing. This helps to mitigate risks and is particularly beneficial for organisations seeking to expand their portfolio into new or exploratory areas
- Increased flexibility: Partnerships offer greater flexibility as they can be formed for specific projects without the need for long-term commitments or broader integration activities. This enables organisations to adapt more quickly to changing market conditions or emerging data
- Access to specialised expertise: Partnerships can expand access to specialised expertise and knowledge. This is particularly beneficial when venturing into new disease areas, technologies or geographies, where your partner's experience and insight can enhance the chances of success
However, many organisations grapple with how to effectively operate within strategic partnerships within R&D.
In order to maximise the benefits and effectiveness of strategic partnerships in R&D, organisations need to adopt a different mindset and approach towards their internal R&D activities. We have identified three key areas where organisations can tailor their working practices within R&D to better support partnership models as a default way of operating and building stronger strategic partnerships. In this way, your organisation can become a recognised and attractive partner of choice for future collaborations.
Building stronger strategic partnerships
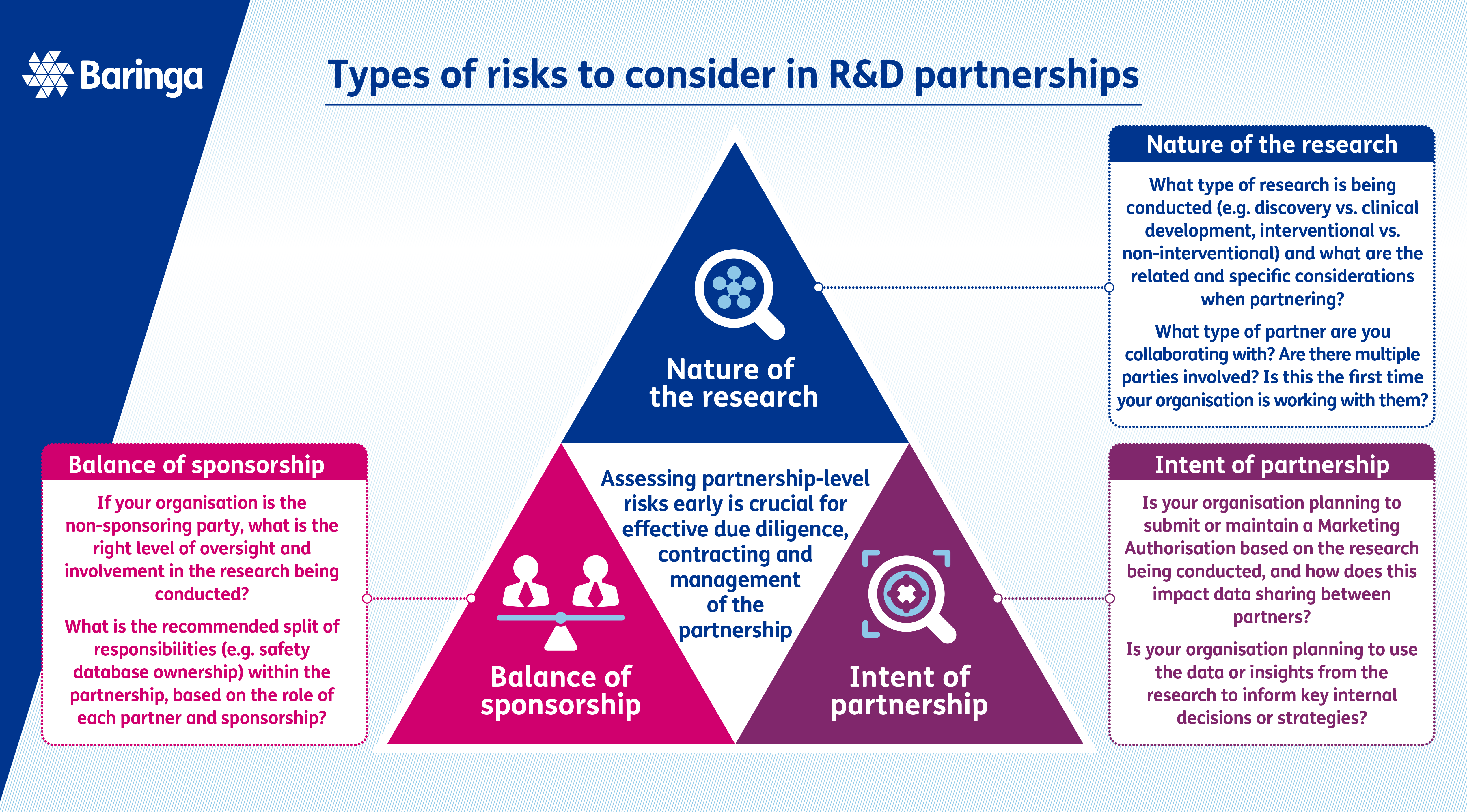
Understanding and managing R&D partnership risks
R&D teams are typically adept in managing research and study-level risks in line with applicable regulations and guidelines, but the collaborative environment introduces new partnership-level risks that need the same comprehension and rigour applied.
To enable this, senior leaders must establish a clear risk appetite for partnership scenarios, which allows teams to understand the ‘guard rails’ for strategic partnerships and translate industry regulations and guidelines into a partnership scenario. This ensures decisions made within partnered R&D activities consistently align with organisational standards and expectations.
To bring this to life, a key decision for any clinical development partnership will be determining the clinical trial sponsorship. If one partner assumes sponsorship for one or more clinical trials as part of an R&D partnership, this introduces the following risks for the ‘non-sponsoring’ partner:
- Reduced control on study decisions which could impact delivery of the asset-level strategy
- Data quality not meeting regulatory expectations for filings
- Knowledge transfer and data transfer activities impacting timelines for filings and launch.
If these risks are identified and discussed early on, partnership teams can proactively implement solutions to mitigate them throughout the collaboration. This can range from defining fit-for-purpose data transfer agreements, to determining the right-sized governance models, through to adapting the level of technical due diligence required for a sponsoring partner. If risks are identified too late, for example after the contract has been executed, there can be more serious consequences that are more challenging to address.
At an enterprise level, establishing clear risk-based principles, guidance, and frameworks can support teams in managing partnership risks. These resources can be used by cross-functional programme teams from the outset, helping them to understand the risk profile and develop appropriate mitigations in line with organisational expectations.
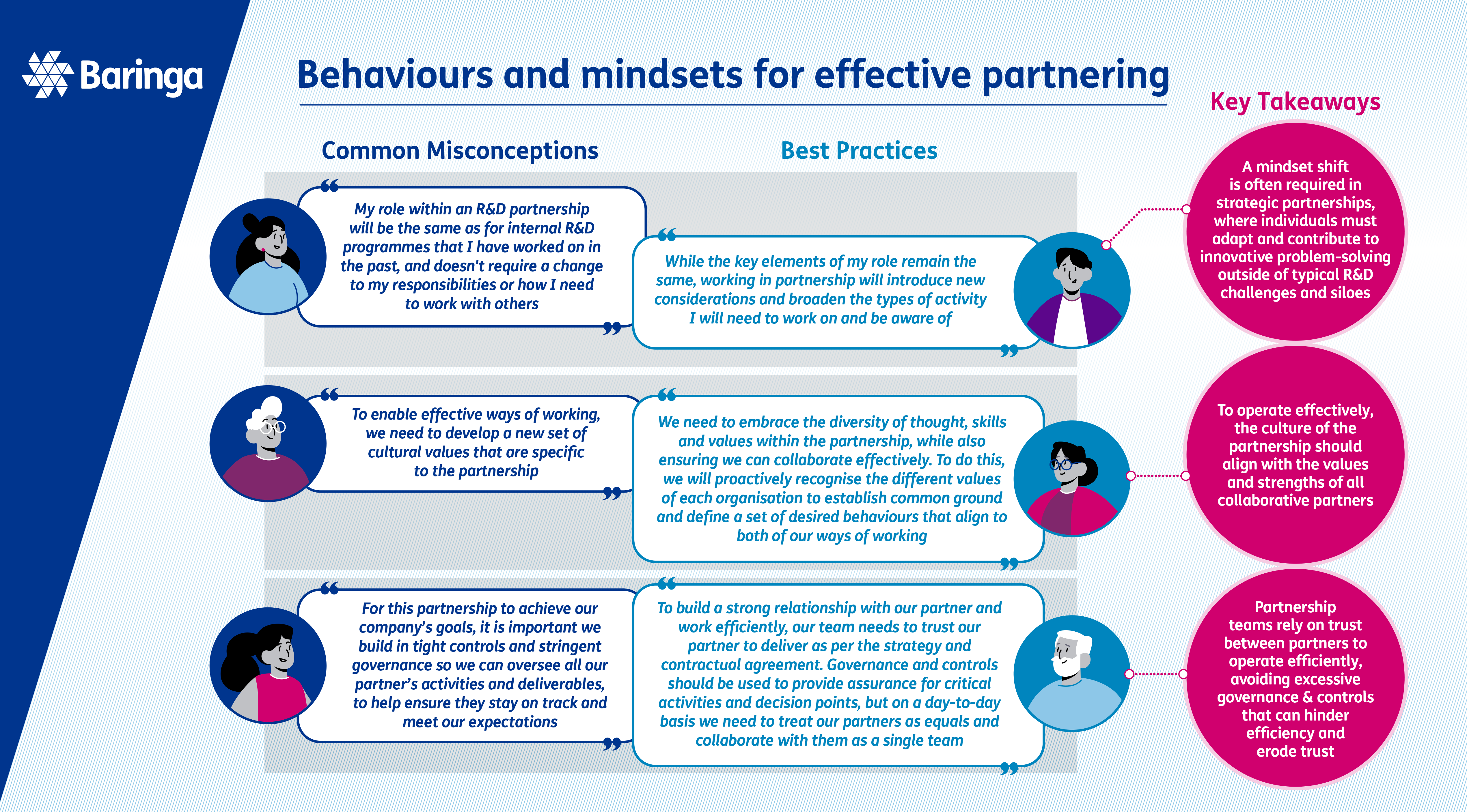
The right team, skills and behaviours
Bringing together the right team, skills and behaviours to support R&D partnerships and build strong relationships.
Organisations often grapple with the challenge of defining appropriate team structures, roles, and responsibilities for different types of R&D partnerships.
The collaborative nature of these partnerships can require a broader range of skills from the team, shifting the focus of traditional R&D team roles in comparison to internal R&D and necessitating stronger involvement from specialised teams such as Alliance Management and Legal.
If roles and responsibilities become unclear, or if the right teams are not involved at the right time, this can have serious consequences and may jeopardise the relationship and overall scientific and business outcomes. To enhance partnership effectiveness, your organisation should define best practices and consistent team structures and roles for operating in this way, which can be tailored to meet the specific needs of each collaboration.
When considering internal team structures and roles for partnerships, it is important to bear in mind the broader set of skills and behaviours that will be required compared to internal R&D programmes. One of the most critical factors for successful strategic partnerships is the quality of the relationship and level of trust with your partner. Both teams and individuals need to have strong relationship management skills, including effective interpersonal communication, cultural sensitivity, and conflict resolution. The complexity of partnerships will also require team members to think and problem solve strategically beyond their areas of expertise to join the dots across partners, internal functions, and leadership.
Repairing a partnership where trust and relationships have broken down can be extremely challenging, underscoring the importance of setting teams up for success from the outset. Joint kick-off sessions at the beginning of a partnership, where teams openly set joint goals and align on behaviours and ways of working, help set the tone of the partnership and foster stronger relationships.
Governance structures and decision-making pathways also significantly impact the relationship and working dynamics between partners, so embedding a fit-for-purpose governance structure that enables swift decision-making is crucial.
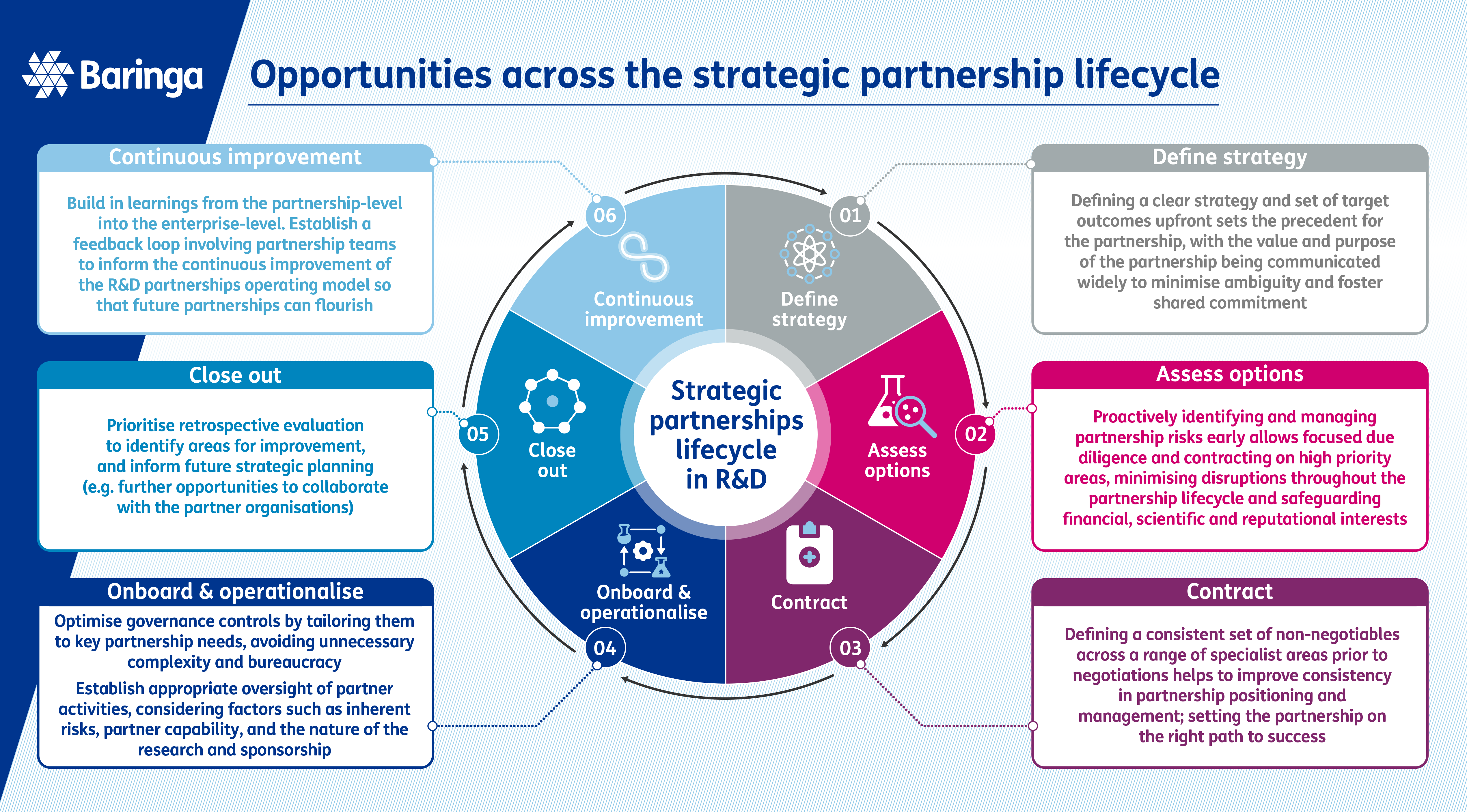
Consistent but flexible processes
Defining consistent but flexible processes for partnerships
While each strategic partnership will be different, they will all share or interact with a set of common processes, including due diligence, contracting, onboarding, health-checks, research/study management, close-out and knowledge transfer. The challenge lies in establishing standardised processes that can be universally applied but are flexible enough to accommodate a variety of partnership models, which can differ in complexity.
For example, the due diligence requirements for a multi-billion-dollar pharma-pharma partnership for a Phase I-III clinical development programme will be very different to the due diligence required for an early research consortium with academic groups. As a result, your organisation may find itself using different, inconsistent processes across different partnerships. This may lead to potential gaps in how important activities such as due diligence are conducted, or teams ’reinventing the wheel’ for each partnership, which may have a significant impact on the success of the partnership or result in serious compliance /legal implications. Defining clear but flexible guidance to avoid duplication and enable teams to focus on high-value activities, rather than deciphering unfamiliar procedures, cannot be understated.
To establish clearer processes for partnering and enhance consistency in handling key activities, the first step is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the types of R&D partnerships within your organisation. It is helpful to assess the volume of partnerships to ensure that focus is directed towards the most relevant areas. For instance, determining the proportion of early research versus clinical development partnerships, identifying if partnerships are more common in specific therapeutic areas, and understanding the ratio between academic and industry collaborations will provide valuable insights that will enable your organisation to prioritise its efforts.
One specific challenge we have observed with our clients as they move towards standardised, yet flexible partnership processes is navigating the IT systems landscape for partnership models. Core R&D systems are often built with requirements focusing on internal activity and do not factor in the complexities and requirements of R&D partnerships. Teams, therefore, may not be able to use certain IT systems and technologies or may need to deploy ‘work arounds’ to use them. This can lead to missing or inaccurate data stored in core R&D systems.
Once partnership types and definitions have been established, your organisation can define process guidance and systems requirements tailored to the specific types of partnerships you engage in, while incorporating the necessary level of flexibility to accommodate the diversity. By establishing consistent ways of working, organisations can streamline operations, improve efficiency, and deliver successful partnerships.
How can Baringa support your R&D strategic partnerships?
We work with the pharmaceutical and life sciences sector to develop and embed effective ways for managing successful R&D partnerships. We typically start with an initial maturity assessment to assess any existing challenges you may have with R&D partnerships and recommend tailored solutions.
More broadly, we can support specific alliance teams to improve their effectiveness and help you develop enterprise-wide solutions to build strategic partnerships across your organisation’s portfolio.
Within a specific partnership, our experts can:
- Set up a new partnership for success by establishing ways of working, identifying risks and embedding a productive and collaborative culture
- Identify and tackle challenges faced with an ongoing partnership, providing actionable recommendations to improve performance in the short- to medium-term.
At the enterprise-level, our experts can:
- Set the vision and strategic intent for R&D partnerships and make sure this is aligned across senior leadership
- Understand and categorise diverse partnership types across R&D
- Develop risk frameworks for collaborative R&D activities
- Tailor team structures for partnership models with the associated skills and behaviours required
- Embed the right culture and behaviours to support effective partnerships
- Set up fit-for-purpose governance structures
- Define flexible processes and ways of working to support the partnership lifecycle.
Contribute to the discussionWe are running a survey to collect industry trends and perspectives on R&D strategic partnerships. If this is a space in which you have worked, please contribute your perspectives via the link below. The survey is anonymous, and we will share the results on our website over summer 2024. |
References
- Armstrong, A. (2023) The 10 highest value R&D projects in biopharma. Available at: https://www.fiercebiotech.com/special-reports/10-highest-value-rd-projects-biopharma (Accessed: 26 June 2024).
- Khalaf, R. (2024) Big Pharma still needs trial success to overcome looming patent panic. Available at: https://www.ft.com/content/5870001c-4fa8-496b-961d-d7b95cfb839a (Accessed: 26 June 2024).
Our Experts




Related Insights

Unlocking the business value from AI in Pharma
Drawing on our experience, we explore four areas where life sciences companies frequently fall short – and outline the critical enablers to achieving both scale and value from AI investments.
Read more
Unlocking the Value of AI in Pharma
Discover how pharma can unlock AI’s full value, boosting innovation, trust, and outcomes through data, governance, and team upskilling.
Read more
The Power of Partnerships across the healthcare ecosystem: how can Biopharma take the lead?
The healthcare ecosystem encompasses a diverse range of organisations with a shared goal: to provide high quality and affordable healthcare. However, as this goal becomes increasingly challenging to maintain, Biopharma organisations play a key role in strategically partnering across the ecosystem to improve health outcomes.
Read more
Optimising Clinical Development ways of working in a strategically outsourced model
Transforming clinical development with a single strategic partner, reducing documentation by 36% and improving oversight and efficiency.
Read moreRelated Client Stories

How Baringa supported Colt Technology with its CRM transformation
Join our TMT Partner Dan Nicholson, as he talks to our client Colt Technology
Read more
We talk to our client KCOM about modernising business operations
Join our TMT Director Sarah Roberts, as she talks to our client Tim Shaw, CEO at KCOM
Read more
Building a trusted data platform to enable scaling and cost savings
How do you accelerate delivery of a £multi-billion network expansion programme using advanced analytics and targeted insight?
Read more
Developing a Target State Operating Model for a technology and language services provider
Developing a comprehensive high-level target state operating model, defining the process architecture, and modelling the necessary capabilities for success.
Read moreIs digital and AI delivering what your business needs?
Digital and AI can solve your toughest challenges and elevate your business performance. But success isn’t always straightforward. Where can you unlock opportunity? And what does it take to set the foundation for lasting success?