The transformative power of Web 3 for investment banks
21 November 2022
Web 3 has the power to transform multiple aspects of the world we live in, including revolutionising the investment banking network.
Web 3’s enablement of decentralised finance (DeFi), the ecosystem that is based upon Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), is the most important development impacting financial services organisations.
In this report we look at these ideas in more detail, focusing on three use cases that we believe present the most immediate benefit for investment banks.
We start with answering three key questions:
- What is Web 3?
- How is DeFi revolutionising the investment banking ecosystem?
- How can investment banks use existing Web 3 technology?
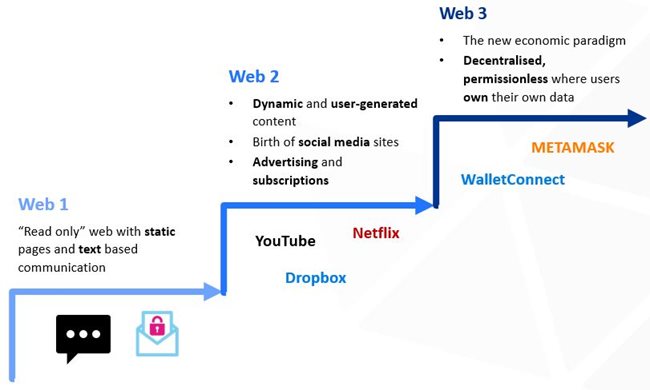
What is Web 3?
The internet has transformed the way we operate in all areas of society, governing what we do and how we do it. Since inception, it has evolved from static sites with minimal user interaction, to the dynamic, user-generated content we have today. Web 3 is the next stage in this evolution, ushering in a new age of the internet.
While an exact definition is often debated, at its heart it's the following three concepts: First, it’s a global decentralised economy, meaning there is no single owner or intermediaries. Second, it’s permissionless – any individual with an internet connection can join and interact over the network. Third, every individual owns their own data – the decision to share data, with which entities and when, is into the hands of the individual. The ‘powered by the people’ characteristic of Web 3 makes it more than just a technology, but also a social movement.
To understand this concept is to understand where the internet comes from:
The power Web 3 has to transform your company is multi-faceted and holistic, and is already having a significant impact on financial services. In a previous article, we look at the six key components that will have the greatest impact on banks, FinTechs, regulators and corporates. Now we focus on one subset of Web 3 – DeFi – and its importance for investment banks.
How is DeFi revolutionising the investment banking ecosystem?
An important subset of Web 3 is the establishment of a new financial system – largely known as decentralised finance, or DeFi. While only a component of Web 3, it’s one of the most material ways that DLT has influenced financial services. Its three core components; distributed ledgers, tokenisation of digital assets and smart contracts are constantly evolving to challenge the status quo:
- Distributed ledgers store immutable entries of asset ownership and transaction history
- Tokenisation divides the ownership of an asset into cryptographically secured digital tokens
- Smart contracts execute verified transactions based on programmable, pre-configured conditions (if x happens, do y).
Rather than the traditional ecosystem of multiple intermediaries, central oversight, and high barriers to participation, DeFi uses a variety of distributed ledger powered applications to revolutionise these concepts. Transaction history is shared amongst all members and offers immutability, meaning records cannot be retrospectively edited. This eliminates the need for central intermediaries and boosts transparency. It also offers the opportunity for entirely new investment opportunities, such as stablecoins and tokenisation.
How can investment banks use existing Web 3 technology?
We’ve already witnessed the disruptive power of these innovations in our article on how Web 3 is transforming the financial services industry globally. In this report, we focus on the impact for investment banks specifically and three use cases where Web 3 technologies are either already being leveraged or where we see future opportunities.
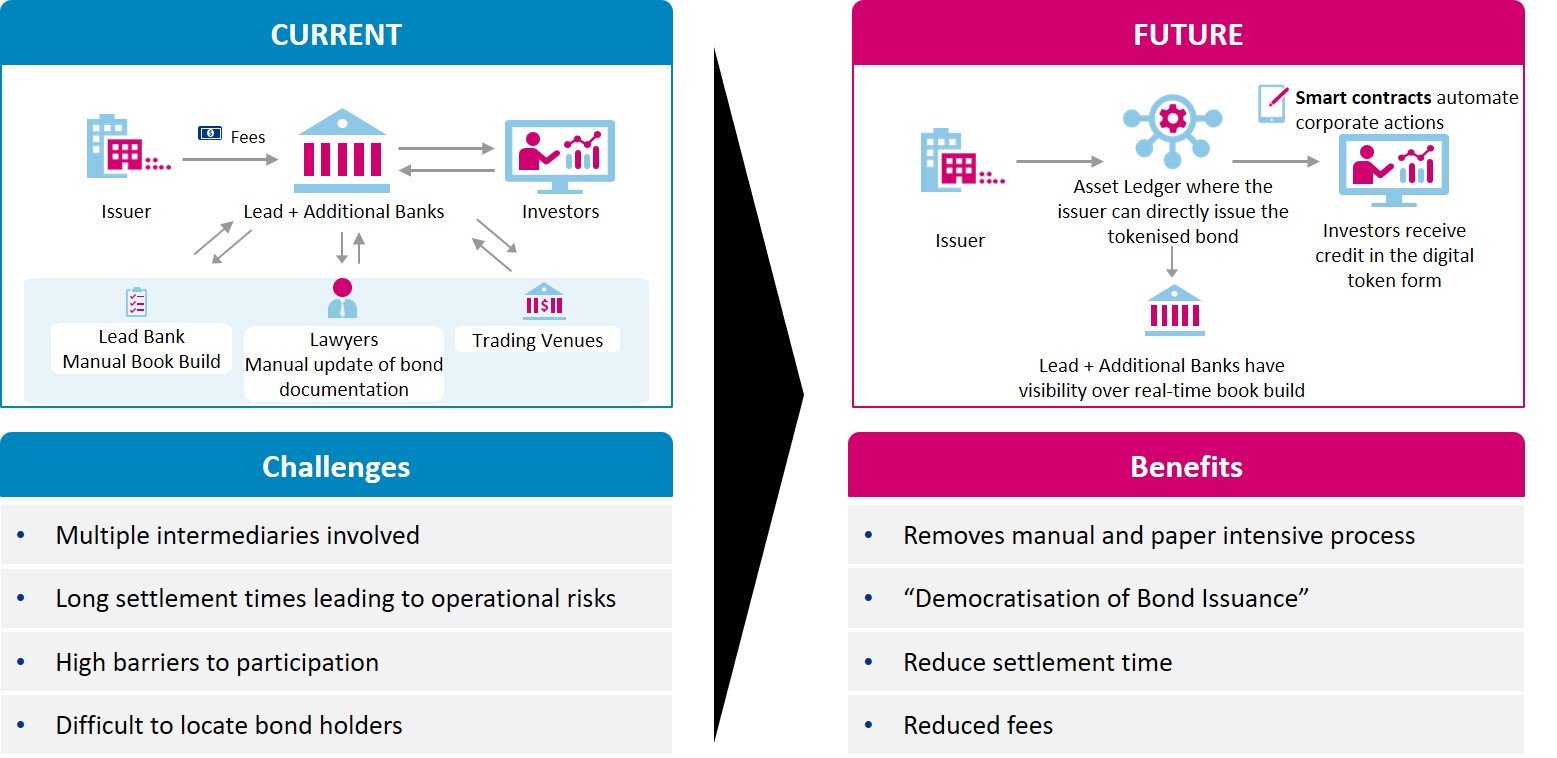
1. Utilising blockchain technology to democratise and streamline new bond issuance
Several investment banks are already leveraging one subset of DLT, in the form of blockchain, and specifically using blockchain technology to issue bonds. The traditional new issuance process often involves costly layers of bureaucracy, long settlement times and unclear ownership post-issuance. Issuing bonds on blockchain reduces all of these inefficiencies. According to Cashlink, the use of blockchain could reduce at least 35% of the cost involved with new issuance by removing the manual and paper intensive documentation process. Smart contract issuance, combined with the speed of blockchain transactions, allows bonds to settle on the same day, rather than the current three days, which in turn reduces settlement risk. By removing some of these barriers to participation, commentators laud this as the “democratisation of bond issuance” where smaller players are able to access the bond markets. This could also have benefits for emerging markets, where small and medium companies sometimes struggle to access funding.
While many banks will have to adapt existing processes, risk modelling and systems to support blockchain issuance, we have already seen this technology successfully utilised and the benefits realised in a series of blockchain issued bonds. Notably, the World Bank issued the first bond via blockchain in 2018, with the European Investment Bank (EIB) following suit 3 years later. More recently, Banco Bilbao Vizcaya Argentaria, Bolsas Mercados Españoles and the Inter-American Development Bank issued Spain’s first blockchain-based regulated bonds. Investment banks have also aided issuance for corporates, including for Singaporean food producer Olam International.
Although there will undoubtedly be a transition period with the usual growing pains, bond issuance is not a stranger to evolution:
"“If you think about the evolution of capital markets and fixed income, we’ve already moved from bearer bonds to the registration of all securities, so this is just the next step that will be the standard, given the efficiencies it brings.”"
Maud Le Moine, head of sovereign, supranational and agency origination in the Investment Banking division of Goldman Sachs
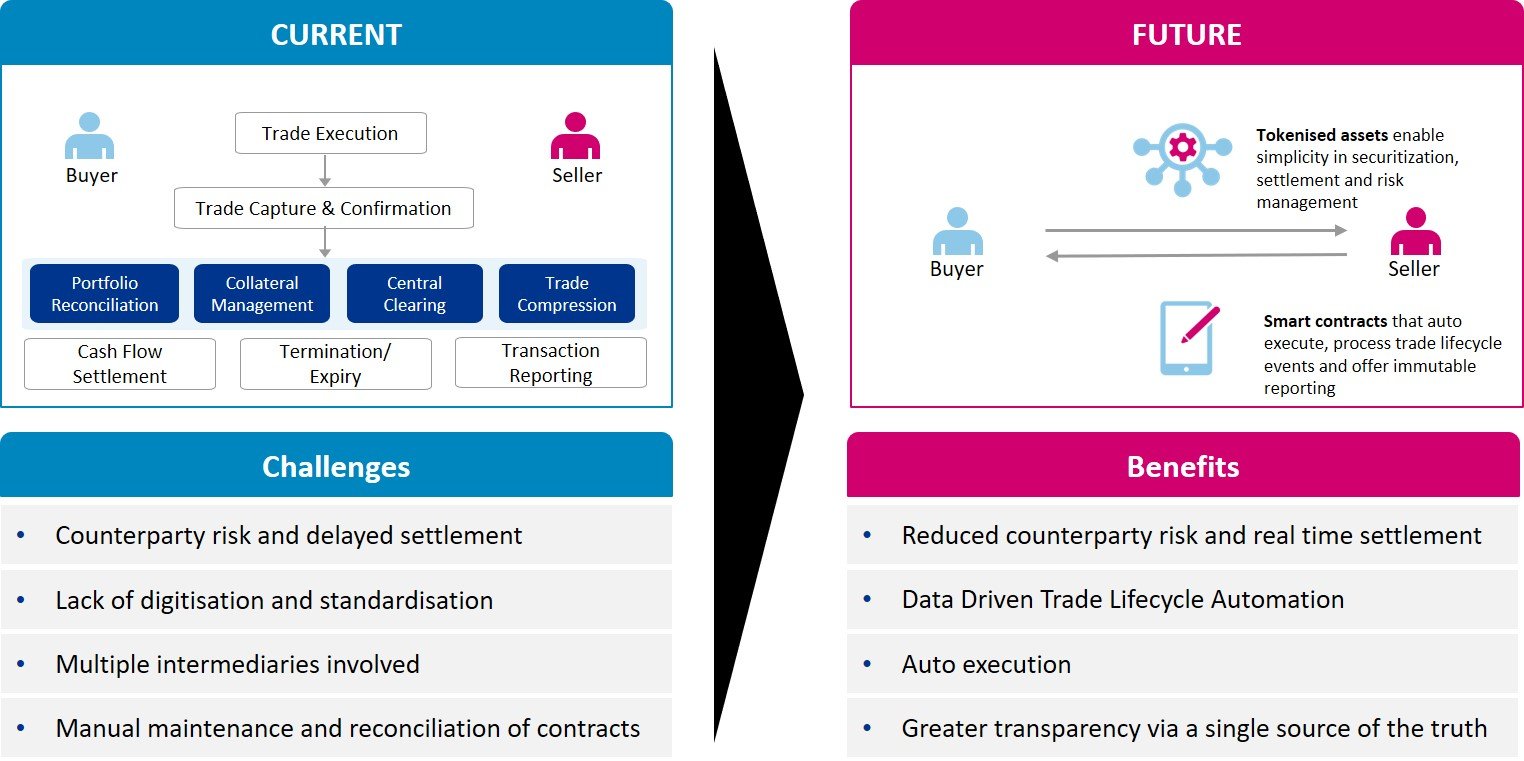
2. Revolutionised OTC derivatives trading via blockchain based smart contracts
While not currently being used, OTC derivative products are a natural use case for blockchain based smart contracts. They are often purely monetary products based on the value of an underlying asset or entity that are bilaterally negotiated between two or more parties. Unlike exchange traded derivatives, OTC derivatives are usually non-standardised, and without a digital footprint, stored as a legal paper contract which is represented in each counterparty’s risk system.
"“The current derivatives infrastructure is hugely inefficient and costly, and there’s virtually no way to implement scalable automated solutions across the industry. That’s because each firm and platform uses its own unique set of representations for events and processes, which requires continual reconciliation of data to ensure the parties to a trade have the same information.”"
Scott O’Malia, Chief Executive of ISDA
Blockchain based smart contracts offer a huge opportunity to transform the OTC derivatives landscape. Smart contracts can digitally represent and self-execute the operational clauses of paper derivative contracts using Boolean logic (if x happens, pay Y). The use of the DLT in the form of Blockchain increases transparency, automates the movement of collateral to reduce counterparty risk, eliminates the need for complex reconciliations and minimises the number of intermediaries involved in today’s $12 trillion market.
3. Intraday liquidity management
In the market context of rising interest rates and quantitative tightening, the associated rising costs of liquidity have brought the optimisation of intraday liquidity into sharp focus for financial institutions. DLT can enable real-time transactions and payment settlement on shared ledgers, which could offer an array of opportunities to address some of the biggest challenges facing active intraday liquidity management.
One of the most prominent challenges facing intraday liquidity managers is understanding their cash and collateral positions across a myriad of accounts in real-time, which impacts the management of risk exposure. These issues are compounded by complex legal entity structures and regulators with a differing regional lens. Existing data processes are typically unable to support efficient real-time account reconciliation and there are significant operational costs to achieve this. Shared ledger technology with account providers, on the other hand, would enable banks to have a real-time view of positions across all accounts. Although not a wide proliferation in the market, notably SWIFT used DLT to enhance their nostro account reconciliation and liquidity management in a proof-of-concept exercise in 2018.1
DLT could support actively traded intraday liquidity markets that would enable banks to effectively smooth their long and short intraday positions. Banks could generate a return on their excess receipts (net credit position), while those with short positions (net debit) can decrease their liquidity exposure and therefore their liquidity buffer requirements. DLT enabled real time settlement would also allow money market transactions to be completed with greater timing certainty and on a minute-by-minute basis. Platforms for intraday liquidity markets using DLT are being developed by a host of market players. Finteum has developed and successfully trialled an intraday FX swaps market with more than 10 global bank participants, ahead of go-live in 2023. Settlement will initially utilise traditional infrastructure, but settlement testing has included fiat-linked digital currencies. Interest from banks has also led Finteum to trial intraday repos on the platform using triparty delivery versus payment (DvP) settlement, without the need for tokenisation. Meanwhile, J.P. Morgan’s Onyx Digital Assets platform enables repo market transactions by tokenising US Treasuries and account balances. 2
For further information, read our article where we discuss at length the opportunities presented by a blockchain technology enabled intraday liquidity market to support active intraday management.
Investment banks must capitalise on the opportunities or risk getting left behind
There is still much uncertainty with the adoption of Web 3 and DeFi down to its market immaturity, lack of regulation and environmental concerns. Despite this, investment banks cannot ignore the opportunities presented. To stay ahead, investment banks must continue to monitor market developments and educate the workforce, to better detect opportunities and strategic partnerships. The opportunities offered can also be nuanced and must be appropriately scoped for each institution.
To help you unpick these challenges, please get in touch with one of our experts; Nick Fulton, Lexi Whomersley or Joshua Buckmaster
References
1 https://www.swift.com/news-events/news/swift-completes-landmark-dlt-proof-concept
2 https://www.ledgerinsights.com/bnp-paribas-joins-jp-morgans-repo-blockchain-platform/
Related Insights

The role of regulators in accelerating Web 3 innovation
Financial institutions are seeing the potential that Web 3 technologies can offer but need the regulatory guard rails to have the confidence to commit.
Read more
Solving the KYC dilemma with Web 3
DLT has great potential to optimise Know Your Customer. We unpack the issues in KYC for retail and corporate banks and evaluate the application of DLT.
Read more
Blockchain opportunities for treasury – disruptive solutions or additional risks?
We take a look at how Web 3 is impacting investment banks, specifically bond issuance, intraday liquidity and in OTC derivatives.
Read more
Why NFTs are here to stay
What is a non-fungible token (NFT)? How will they impact the banking industry, and are they here to stay? In this article, we will dig into these questions.
Read moreIs digital and AI delivering what your business needs?
Digital and AI can solve your toughest challenges and elevate your business performance. But success isn’t always straightforward. Where can you unlock opportunity? And what does it take to set the foundation for lasting success?