
Payment innovations: where should you invest?
5 min read 6 December 2023
Currently the global payments market is worth an estimated $2.2 trillion USD and is growing at 11 percent per year, with that growth showing no sign of slowing down. Crunchbase data has shown that global investment in payments startups reached $38.5 billion USD in 2022. This growth is leading to new opportunities, and investment in payment innovation, such as real-time payments, smart contracts and tokenisation. Today, payment innovation is playing an important role for global businesses and financial institutions (FIs) looking to transform their payments functions to maximise their value and significantly contribute to the organisation’s profits, whilst simultaneously reducing costs.
Given the large volume of changes, owners of payment portfolios are asking themselves where their organisation should invest their time, money and resources. It is important to understand where innovations are genuinely differentiating opportunities versus the ‘nice to haves’. These need to be balanced alongside meeting the non-discretionary demands from compliance, regulatory and schemes.
In the matrix and article below, we explore the payment innovation ecosystem and provide guidance for those in the industry, by outlining key innovations, that we believe will have the most significant impact on the payments market.
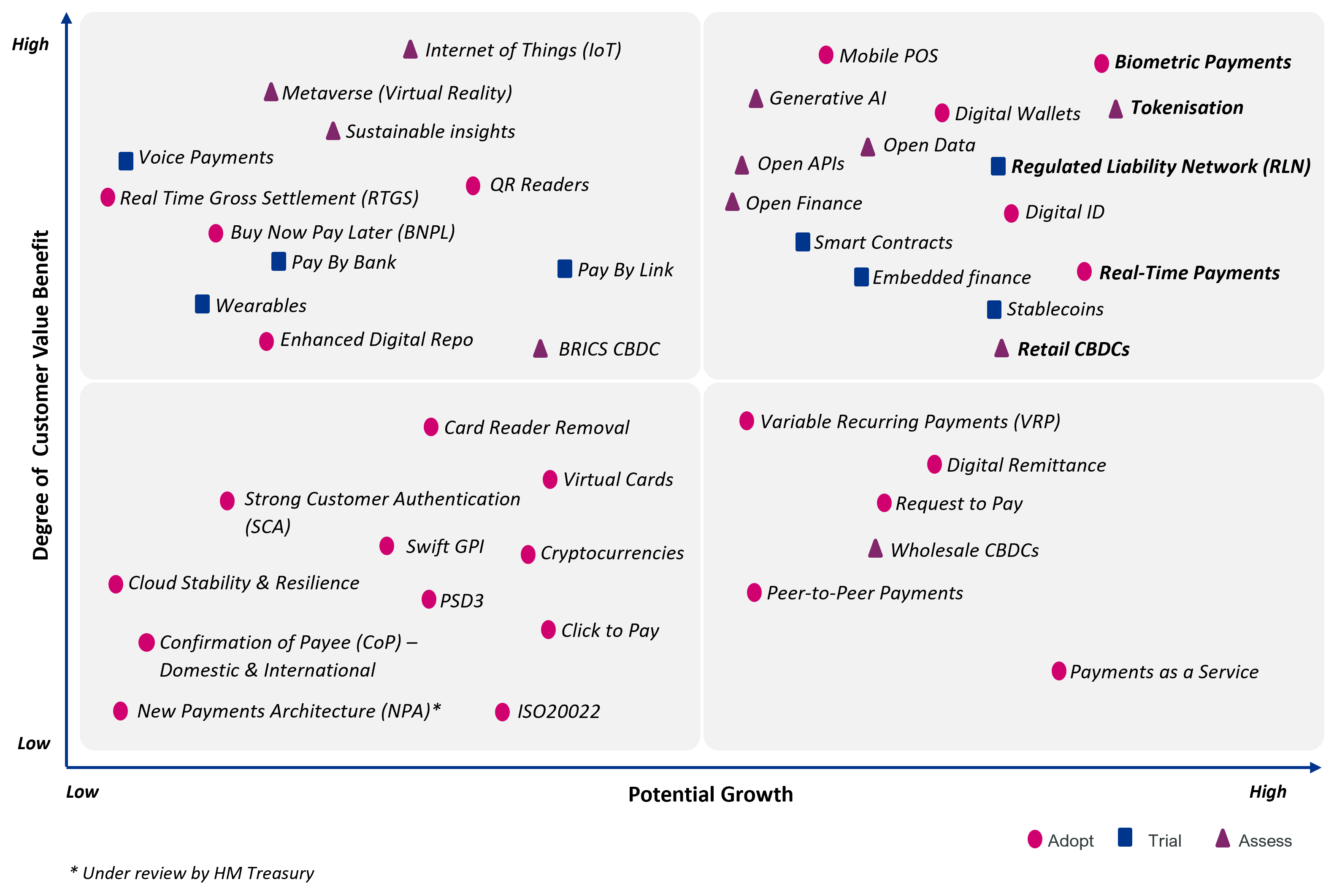
Adopt: innovation should be incorporated into the organisation’s payments proposition.
Trial: the organisation should consider running or joining a pilot program to evaluate the innovations suitability for the specific use cases identified.
Assess: the organisation should evaluate the potential benefits and risks of the innovation before making a decision to trial or adopt it.
We have explored a wide range of payment innovations. In the table below we have identified specific opportunities which we believe should be considered within change portfolios in the future. These innovations have a high potential to generate revenue whilst also delivering an improvement in customer experience.
Payment innovations opportunities
Biometric payments
What is it?
A payment authentication method that leverages biometrics, such as fingerprints, facial and voice recognition.
What can it do?
Biometric payments are becoming increasingly popular, as they offer a more convenient and secure method of making and accepting payments, streaming the customer eCommerce checkout experience.
What impact will it have on financial services (FS)?
The global market is expected to reach $3.4 bn in 2025 (Market Research Future), with Payments Intelligence outlining nearly 60% of US consumers used biometric authentication to make online purchases in November 2023.
Biometrics payments have the potential to enhance security, convenience and customer experience, by enabling transactions to be completed without the need for a physical card. Therefore these payments are considered more secure than traditional authentication methods, as biometric data is unique and more difficult to forge or steal.
What actions should you take in the next 12 months?
A key consideration for biometric payment is the interoperability with payments acceptance devices and processing platforms to enable and facilitate a seamless user experience. This interoperability will require standardised requirements and collaboration between key industry partners. These partnerships will help to reduce the complexity and cost of implementation for Fis.
Therefore, FIs need to:
- Consider the consumer needs and preferences, for biometric modality as there are varying levels of accuracy within the market
- Evaluate their current technology stack to determine whether the target solution is interoperable with existing infrastructure
- Assess the data protection regulations for the collection and processing of biometric data
Regulated Liability Network (RLN)
What is it?
The RLN concept provides an alternative approach to progress the financial market ecosystem, through the adoption of distributed ledger technology (DLT), with central bank money, commercial bank money and electronic money on a regulated settlement substrate.
What can it do?
The RLN has the potential to provide a multi-asset, 24/7/365, interoperable, global financial market infrastructure (FMI) for payments and settlement.
What impact will it have on financial services (FS)?
The RLN concept seeks to introduce the benefits of new technologies such as DLT and tokenisation in a regulated Distributed FMI. It would look to protect the current regulated financial ecosystem and provide partitions to commercial, central bank e-money and potentially regulated stablecoins on a settlement substrate. It has the potential to facilitate new settlement functionality in the payment space and also drive cross-border payment benefits.
What actions should you take in the next 12 months?
The RLN is gaining momentum globally having already run successful proof of concepts (PoCs) on cross-border payments with plans for domestic and multi-asset use cases in further research.
Global payments architecture initiatives such as the Digital Pound are already considering how they may interact with the RLN and so should the private sector.
Financial services firms need to consider how their technology stacks integrate with new FMIs and also participate in the shaping of them. It will be strategically important for participants to closely monitor of how this area develops and consider what it means for their payments approach.
Retail CBDCs (rCBDCs) for Cross Border Payments
What is it?
A currency issued by a central bank that can be used by the general public to make and accept payments.
What can it do?
rCBDC designs are seeking to incorporate new functionalities such as micro payments or programmable payments.
This may allow for a host of new payments opportunities such as more complex payment conditionality.
What impact will it have on financial services (FS)?
This functionality may allow some new or refined business models to emerge based on new technologies such as an approach to pay for individual pieces of content through micro-payments.
It may also drive competition for retail banks to provide new functionality that provides consumer benefits.
What actions should you take in the next 12 months?
The Digital Pound is one of many rCBDCs progressing globally and their introduction appears to be a matter of ‘when’, not ‘if’.
Participants in the retail space will need to closely consider how these functionalities will impact their consumers and how they may impact their own technology stack.
There will likely be first mover advantages here so early participation and testing will be particularly pertinent.
Tokenisation
What is it?
The process of transforming ownership rights for an asset into a digital token. Tokens can be stored on either centrally governed or distributed ledgers such as blockchain.
What can it do?
Tokenisation has numerous use cases within the payments market, including: enabling atomic settlement, streamlining international trade and the speed of securities financing, such as repurchase agreements.
What impact will it have on financial services (FS)?
The impact on financial services is interesting as there are significant benefits to tokenisation, such as the access of assets to a wider customer base, improving efficiency in clearing/settlement and reducing data breaches due to fraud. However, for benefits to be materialised and financial markets to maintain functioning through adoption, there needs to be sufficient liquidity on-chain or versatile on/off-ramps.
What actions should you take in the next 12 months?
The market is a long way from mass adoption of tokenisation, although there is a growing volume of examples and to get there would require several changes:
- Technical connectivity – interoperability is needed to deliver safer, faster and cheaper services in a way that the participants are comfortable to follow, e.g. agreeing the potential role of bridges between chains
- A clear business case – some of the inefficiencies in settlement processes can also be how FIs make money so finding the right commercial model will be essential
- Industry dialogue - FMIs, FIs, regulators and others need to work together to avoid too many siloed initiatives and liquidity fragmentation
- Standards – alignment around defined standards is essential to drive consistency and help to support progress
Real-time Payments (RTP)
What is it?
A streamlined payment system enabling near-instantaneous transfer of funds between individuals, businesses, and institutions.
What can it do?
Real-time payments are rapidly growing in emerging markets, with the primary use case being paying for everyday expenses such as food shops or bills.
What impact will it have on financial services (FS)?
The UPI system in India is one such example and the technology has shown scale with over 46 billion transactions being processed in a single day.
According to Juniper Research the value of real-time payment transactions is expected to reach $44 trillion per annum by 2026.
The impact on FIs will lead to greater efficiency when making a payment, improved customer experience and provide challenge to the incumbent card rails to drive value to banks and merchants, as stated in the Future of Payments Report.
What actions should you take in the next 12 months?
There have been successful implementations of RTPs globally, but to do so FIs need to ensure that their infrastructure can support the high volume and speed of these transactions. This will likely mean that payments architecture modernisation is required for both FMIs and FIs.
Therefore, FIs need to:
- Consider whether the current payments infrastructure is suitable for end consumers current demands and whether the market should be investing in real-time payment infrastructures over and above other payment types
- Determine whether education is required for customers to improve the adoption and utilisation of real-time payments
- Evaluate their current technology stack to determine whether the target solution is interoperable with their existing infrastructure
- Comply with all applicable regulations, for example anti-money laundering (AML) and financing terrorism (CFT)
The payments landscape is constantly evolving, with new players introducing new innovations frequently into the ecosystem. As a result, owners of payments portfolios need to ensure effort is spent in the right place.
Therefore it is important to:
- Understand the problems that the innovation will solve – what are the use cases for the innovation and how will end customers benefit from it
- Research the innovations regulatory requirements and the potential timeline to its maturity
- Identify the implications of the innovation on your current product offering and future payments strategy
- Assess whether the innovation is complementary to your existing payments architecture
- Determine whether any operating model changes are required to support the product or technological change – what are the efficiencies that can be leveraged?
We have only briefly skimmed the large scale of innovation within the payments market. However, it is important to be cognisant of the payment regulators and their role in establishing guardrails for future innovation. Further to this, effecting real change in the market, requires collaboration. Cross-industry participants need to work together to define and deliver solutions that work for end consumers. For example, Open Banking and the role of the CMA9, the CBDC pilots, global sandboxes or the experimentation phase that will be run by UK Finance for RLN. Whilst FIs need to assess the innovations and decide which will be part of their future roadmap, they also need to consider the part they will play in shaping the future payments market and effecting real change.
Our Experts


Related Insights

Striking the balance: Regulation and innovation in payments
As we look ahead to the Payments Vision Delivery Committee's Q2 2025 announcement, we ask: can we ever truly balance regulation and innovation in payments?
Read more
Reflections on the UK's National Payments Vision
We share our view on the UK's National Payments Vision and uncover what it means for the wider payments landscape.
Read more
Meet the payments leader of the future
Traditional banks are starting to realise the huge revenue-generating potential of their payments functions and are transforming their operating models, embracing new technologies, and ushering in fresh ways of working. But there's a piece of the puzzle remaining: people.
Read more
Why banks need to evolve their legacy payments operating models
Evolving your payments operating model could hold the secret to greater customer-centricity and value creation. Discover our three steps to building a strategy centered on innovation and growth.
Read moreIs digital and AI delivering what your business needs?
Digital and AI can solve your toughest challenges and elevate your business performance. But success isn’t always straightforward. Where can you unlock opportunity? And what does it take to set the foundation for lasting success?